- java.lang.Object
-
- org.jenetics.ProbabilitySelector<G,C>
-
- org.jenetics.ExponentialRankSelector<G,C>
-
- All Implemented Interfaces:
- Selector<G,C>
public final class ExponentialRankSelector<G extends Gene<?,G>,C extends Comparable<? super C>> extends ProbabilitySelector<G,C>
An alternative to the "weak"
LinearRankSelectoris to assign survival probabilities to the sorted individuals using an exponential function.
where c must within the range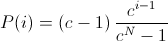 ,
,
[0..1).A small value of c increases the probability of the best phenotypes to be selected. If c is set to zero, the selection probability of the best phenotype is set to one. The selection probability of all other phenotypes is zero. A value near one equalizes the selection probabilities.
This selector sorts the population in descending order while calculating the selection probabilities.
- Since:
- 1.0
- Version:
- 2.0 — $Date: 2014-12-28 $
- Author:
- Franz Wilhelmstötter
-
-
Constructor Summary
Constructors Constructor and Description ExponentialRankSelector()Create a new selector with default value of 0.975.ExponentialRankSelector(double c)Create a new exponential rank selector.
-
Method Summary
All Methods Instance Methods Concrete Methods Modifier and Type Method and Description booleanequals(Object obj)inthashCode()protected double[]probabilities(Population<G,C> population, int count)This method sorts the population in descending order while calculating the selection probabilities.StringtoString()-
Methods inherited from class org.jenetics.ProbabilitySelector
probabilities, select
-
-
-
-
Constructor Detail
-
ExponentialRankSelector
public ExponentialRankSelector(double c)
Create a new exponential rank selector.- Parameters:
c- the c value.- Throws:
IllegalArgumentException- ifcis not within the range[0..1).
-
ExponentialRankSelector
public ExponentialRankSelector()
Create a new selector with default value of 0.975.
-
-
Method Detail
-
probabilities
protected double[] probabilities(Population<G,C> population, int count)
This method sorts the population in descending order while calculating the selection probabilities. (The methodPopulation.populationSort()is called by this method.)- Specified by:
probabilitiesin classProbabilitySelector<G extends Gene<?,G>,C extends Comparable<? super C>>- Parameters:
population- The unsorted population.count- The number of phenotypes to select. This parameter is not needed for most implementations.- Returns:
- Probability array. The returned probability array must have the
length
population.size()and must sum to one. The returned value is checked withassert(Math.abs(math.sum(probabilities) - 1.0) < 0.0001)in the base class.
-
-